What is a UPS?
UPS Stands for Uninterrupted Power System, its duty is to be ready to deliver power when an outage happens in the operation. The base of an UPS is an array of batteries, and the quantity of batteries depend on the level of voltage and capacity the process needs.
“The tendency in the Underground Mining Sector technologies is to increase the automation of the processes as well as the quick deployment of the solutions in their day-to-day operations, and all this should be based on the reliability that the components of those systems must have”. Eng. Edgar Carrillo Rendon
Extending the Life of a UPS
It is necessary to clarify what a UPS requires to be reliable and have a long life and to offer the number of cycles that the batteries are designed to resist.
We often see some batteries in the backup system swollen which is due to overcharging. This condition discomposes the water in the electrolyte, producing gases and finally expanding the battery enclosure—causing the batteries to swell.

Source: https://www.researchgate.net/
What Makes a Reliable UPS?
We think that a reliable UPS should have separated power supplies: one to charge the batteries and another to keep the load working.
Why is this important? Sometimes, people think that a standard DC Power Supply is enough to charge batteries and keep the load ON which is a big mistake. The batteries require a variable voltage and current level to fulfil their charging requirements.
A battery faces at least three phases or states.
- Stage 1 is named the I-phase. This phase is where a high constant-current stage is transferred to the battery, also is maned bulk charge stage. A battery faces this stage when it is deeply discharged. In this stage, the charger provides its maximum output current. The battery absorbs the charge raising the voltage level.
- Stage 2 is named the Uo-phase. The battery faces a constant-voltage boost stage, absorption stage, or topping charge in this phase. It continues being charged at a constant over-voltage. This voltage level decreases when the battery reaches 95% of its capacity.
- Stage 3 is named the U-phase or float charge state. In the float-voltage phase, the voltage is reduced to a safe value for long periods of time (weeks) without significantly reducing the battery’s lifetime. This happens to compensate for the loss of charge as a battery with standard self-discharge behaves.
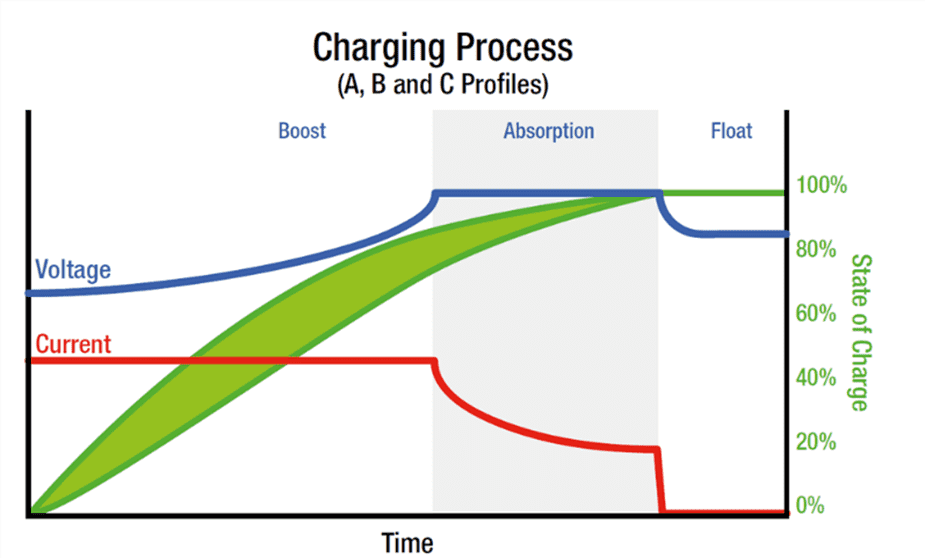
Source: https://www.redarc.com.au/
After understanding the three phases of the battery charge, do you still agree that a regular power supply is enough to keep a battery system charged?
The Solution: The Firefly UPS Control Panel by IoT Automation
The FireFly UPS can support a smart lighting system with low power consumption and is engineered to support the deployment of FireFly Smart Lighting. It also serves as a communications hub that can be easily and affordably deployed to the operational mining areas.
The FireFly UPS control panel is an intelligent decentralised power system designed specifically to drive underground industrial LED lighting circuits and support other DC powered communications systems, such as Network Infrastructure and some Leaky Feeder systems.
It supplies a +48VDC power feed which can drive four individual strings of FireFly LED lights at 30 modules per string. Its battery backup setup is equipped with a +48VDC 50Ah system, which supports around six to eight hours run time for each string of FireFly LEDs when the main power is turned off.
The modular UPS panel is secured to the mine wall via chains or rock bolts and is constructed from powder-coated stainless steel and a roll cage to protect the unit. Furthermore, its internal components can be interchanged to suit the required function and assist with maintenance and repairs.

